IUSE STEM GRANT 2015-2019 AWARD
Investigators: Andreas Spanias(Arizona State University), Mahesh Banavar(Clarkson University)
 The NSF IUSE project is based on a close collaboration between the School of Electrical Computer and Energy Engineering (ECEE), the interdisciplinary School of Arts, Media and Engineering (AME) at Arizona State University (ASU), and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Clarkson University (CU). It also includes close collaboration with consultants from Johns Hopkins University (JHU), Prairie View A&M University (PVAMU), the Phoenix (Community) College (PC), Temp Corona Del Sol high (CDS) school, as well as a collaboration with participants from the Clarkson University Office of Education Partnerships, St. Lawrence University, and the industry partner Sprint. The project addresses motivating students to pursue studies in STEM areas by creating and disseminating scalable modules that demonstrate how math and engineering theory enables modern applications.
The NSF IUSE project is based on a close collaboration between the School of Electrical Computer and Energy Engineering (ECEE), the interdisciplinary School of Arts, Media and Engineering (AME) at Arizona State University (ASU), and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Clarkson University (CU). It also includes close collaboration with consultants from Johns Hopkins University (JHU), Prairie View A&M University (PVAMU), the Phoenix (Community) College (PC), Temp Corona Del Sol high (CDS) school, as well as a collaboration with participants from the Clarkson University Office of Education Partnerships, St. Lawrence University, and the industry partner Sprint. The project addresses motivating students to pursue studies in STEM areas by creating and disseminating scalable modules that demonstrate how math and engineering theory enables modern applications.
The Collaborative IUSE Education Project involves:
- Creating and disseminating mobile and scalable modules that will motivate and reinforce STEM education.
- Enabling and motivating undergraduate students to learn STEM topics by algorithm understanding and provide programming skills for high-tech workforce creation.
- Designing theory, applications, software and hardware integrated modules that can be immersed in existing STEM courses (e.g. in ASU EEE407 and CU EE401 DSP) and non-STEM courses.
- Comprehensive outreach effort that includes universities, community colleges, HBCUs, Hermanas Conferences, and high schools.
Primary Goals
- Making students proficient in modern algorithms enabling them to relate basic STEM topics to high tech products.e.g. Fourier and MP3, Iphone and Spectra
- Developing STEM algorithm modules with focus on Sensor Networks using modern handheld technologies(e.g. smartphones, tablets etc.)
- To create and embed STEM content in modules in a manner that helps in developing desired skills.
- Encouraging more students to enroll in STEM majors in college.
IUSE Workshops 2016 – 2020
Publications
- B. Ayotte, J. Au-Yeung, M.K. Banavar, D. Barry, G. Muniraju, S. Rao, A. Spanias, C. Tepedelenlioglu, “Introducing machine learning concepts using hands-on Android-based exercises,” IEEE/ASEE Frontiers in Education (FIE) (accepted), 2019.
- V.S. Narayanaswamy, U.S. Shanthamallu, A. Dixit, S. Rao, R. Ayyanar, C. Tepedelenlioglu, A.S. Spanias, M.K. Banavar, S. Katoch, E. Pedersen, P. Spanias, P. Turaga, F. Khondoker, “Online Modules to Introduce Students to Solar Array Control using Neural Nets,” A2019 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, June 2019.
- Chao Wang, Abhinav Dixit, Andreas Spanias and Sunil Rao, “Introducing Machine Learning in a Sophomore Signals and Systems Course”, Frontiers in Education, Cincinnati, October 2019.
- Blaine Ayotte, Justin Au-Yeung, Mahesh K. Banavar, Dana Barry, Gowtham Muniraju, Sunil Rao, A. Spanias, C. Tepedelenlioglu, “Introducing machine learning concepts using hands on Android-based exercises”, Frontiers in Education, Cincinnati, October 2019
- M.K. Banavar, S. Rivera, D. Barry, “Mobile apps for Incorporating Science and Engineering Practices in K-12 STEM Labs,” IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), San Jose, CA, October 2018.
- M.K. Banavar, S. Rivera, B. Ayotte, K. Mack, A. Spanias, C. Sahu, “Teaching Signal Processing Applications using an Android Echolocation App”, IEEE Transactions on Education (submitted), 2019.
- S. Ranganath, J. Thiagarajan, D. Rajan, M. Banavar, A. Spanias, J. Fan, K. Jaskie and C. Tepedelenlioglu, “Interactive Signal Processing Education Applications for the Android Platform,” ASEE Computers in Education Journal, 2019.
- U. Shanthamallu, S. Rao, A. Dixit, V. Narayanaswamy, J. Fan, A. Spanias, ” Introducing Machine Learning In Undergraduate DSP Classes,” IEEE ICASSP 2019, Brighton, UK, May 2019.
- V Narayanaswamy, U Shanthamallu; A Dixit, S Rao; E Pedersen; P Spanias; P Turaga; F Khondoker, R Ayyanar, C Tepedelenlioglu, A S Spanias, Mahesh K Banavar, Sameeksha Katoch, “Online Modules to Introduce Students to Solar Array Control using Neural Nets,” Proc. ASEE 2019 paper, Tampe Bay, June 2019
- A. Dixit, J. Fan, S. Katoch, U. S. Shanthamallu, G. Muniraju, S. Rao, M. Banavar, P. Spanias, A. Spanias, Andrew Strom, “Multidisciplinary Modules on Sensors and Machine Learning” in American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE), Salt Lake City, Utah, 2018.
- A. Dixit, U. S. Shanthamallu, A. Spanias, V. Berisha, and M. Banavar, “Online Machine Learning Experiments in HTML5” in IEEE Frontiers In Education(FIE),San Jose, California, October 3-6, 2018. (Accepted)
- Benjamin Robistow, Robert Newman, Thomas DePue, Mahesh Banavar, Dana Barry, Paul Curtis, Andreas Spanias, “REFLECTIONS: AN E-MODULE FOR ECHOLOCATION EDUCATION”, 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, March 2017.
- A. Dixit, S. Katoch, P. Spanias, M. Banavar, H. Song, A. Spanias (2017). Development of Signal Processing Online Labs using HTML5 and Mobile platforms. 2017 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Indianapolis, October 2017
- Andreas Spanias, Mahesh Banavar, Photini Spanias, Henry Braun, Yongpeng Zhang (2016). Development of Course Modules for Multidisciplinary STEM Education. 2016 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Pennysylvania, October 2016.
- K. Mack, M.K. Banavar (2017). Teaching Ranging and Localization using Bluetooth on Android Devices. 2017 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE).
- M.K. Banavar, H. Gan, B. Robistow, A.Spanias (2017). Signal Processing and Machine Learning Concepts using the Reflections Echolocation App. 2017 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE).
- Thomas H DePue, Robert Newman, Benjamin Robistow, Paul Curtis, Kevin Mack, Mahesh Banavar, Tianqi Yang, Dana Barry, Andreas Spanias, Whitni Watkins (2016). An Android App for Spatial Acoustic Analysis as a Learning Tool. 2016 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Pennysylvania, October 2016.
Posters presented at Recent Events
PhotoGallery: ASU undergraduates
PhotoGallery: University of Cyprus undergraduates
Lecture at SOAR () North Country class
J-DSP in HTML5
Award winning J-DSP online laboratory, provides a valuable online resource for DSP simulation for several years. Elevated requirements for online education content has motivated rebuilding and enhancing online simulation tools in an entirely new and secure framework. With no browser dependencies and environment similar to a web-site, J-DSP in HTML5 can work directly connected with the Internet.
 J-DSP in HTML5 provides new simulation environment to our award-winning J-DSP online laboratory with better look, better performance and latest technology. The Web 4.0 environment of J-DSP in HTML5 provides several opportunities to incorporate new data and cloud interfaces that enable to develop several exercises with real time hardware processing. The new interface enables entirely new educational experience and several new functionalities such as:
J-DSP in HTML5 provides new simulation environment to our award-winning J-DSP online laboratory with better look, better performance and latest technology. The Web 4.0 environment of J-DSP in HTML5 provides several opportunities to incorporate new data and cloud interfaces that enable to develop several exercises with real time hardware processing. The new interface enables entirely new educational experience and several new functionalities such as:
- Ability to perform DSP operation over large set of datasets.
- Allowing to demonstrate more clearly, frequency resolution, spectral leakage in Fourier analysis and more complex time-frequency graphics such as spectrograms.
- Data acquisition from remote devices like mobile phones and perform DSP operations over it in real-time.
- New opportunities to interface with other devices like computers, Android phones and iPhones.
- Interface with various hardware platforms like ArduinoTM, Raspberry Pi and the NXP sensor boards.
- Capability can be used for explaining and demonstrate complex machine learning algorithms.
- Ability to track parameters and the performance of algorithms from remote devices will provide students experience in areas such as the Internet of Things (IOT).
To check out the J-DSP Modules and Demos, click here.
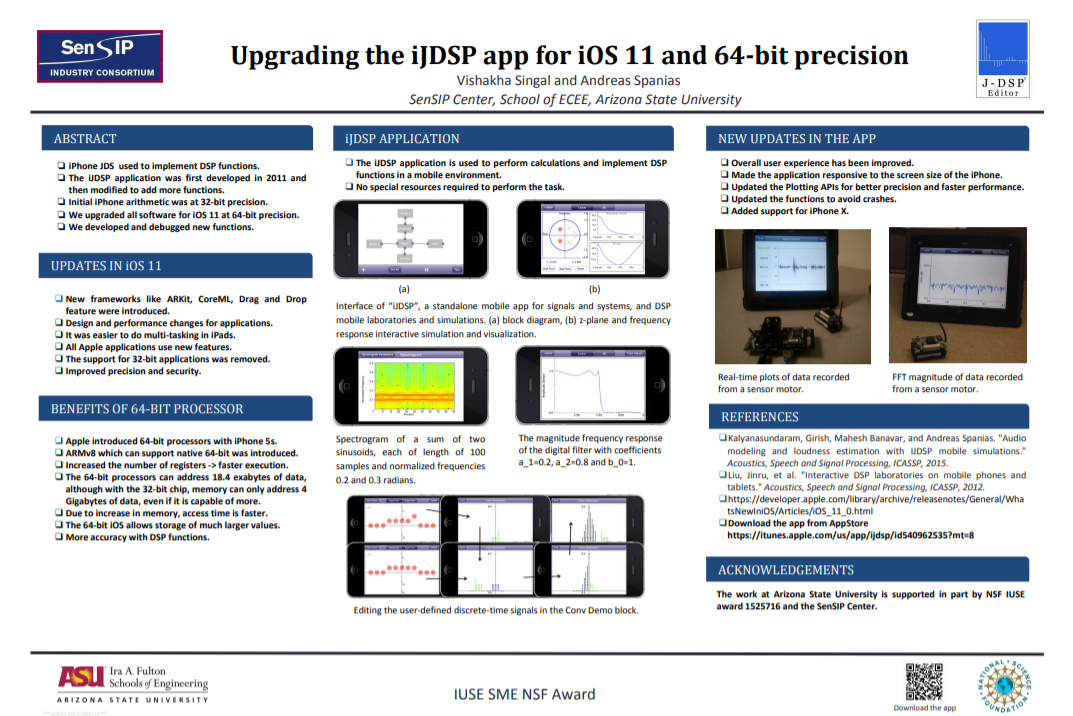
Online Machine Learning Experiments – Speech Formant Extraction and classification
Development of online machine learning software along with an exercise in speech processing for use in the DSP class: A series of HTML5 interactive blocks were developed and used to support a computer exercise that provided learning experiences in linear predictive coding of speech and in using machine learning for phoneme recognition. The primary objective is to provide a machine learning experience to undergraduate students. The functions and simulations described, provide a user-friendly visualization of phoneme recognition tasks which makes use of the Levinson-Durbin linear prediction algorithm and the k-means machine learning algorithm. The exercise was assigned as a class project in our undergraduate DSP class. Our assessment results were encouraging and demonstrated learning of several new concepts in the undergraduate class and association of these concepts with UG DSP theory. The exercise and the associated interactive graphical user interface energized the students many of whom discussed their results in class and posed several “what if” questions.
- Machine Learning blocks in JDSP HTML 5 performs Speech formant clustering and classification in real time
- The first 2 speech formants are extracted in real time from a speech signal
- Linear Predictive Coding is used to estimate the spectral envelope for a given frame
- Students can easily learn, visualize, and experiment with signals and implement real-time DSP applications that integrate Machine learning in JDSP-HTML5
Assessment
ECHOLOCATION ON ANDROID

- Audio based app designed for Android devices.
- Promotes learning the signal processing basics like correlation,convolution, FFT for fast computation etc.
- Includes assistance for visually impaired.
Reflections app for echolocation and echolocation education. To know more, click here.
BLUETOOTH LOCALIZATION

- Promotes learning in concepts such as triangulation and localization.
- Localization done on Android devices using Bluetooth RSSI.
OUTREACH
- Includes workshops and In-class activities designed for undergraduate students.
- Includes collaboration with universities namely John Hopkins University, Prairie View A&M and University of Washington Bothell.
- K-12 engagement includes collaboration with high schools(e.g. Corona Del Sol High School) and Community Colleges(e.g. Phoenix College, SUNY Canton) as well.
SENSOR NETWORKS
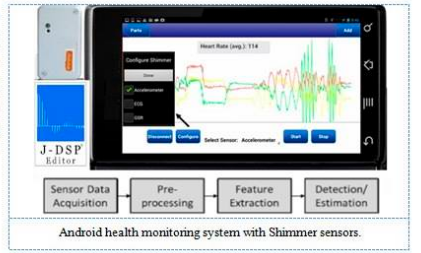
- Provides skill development across various hardware and software platforms.
- Laboratory exercises are developed with Android, Java, HTML, iOS, MATLAB, LabVIEW, Tiny OS, NesC and TI DSP Assembly.
- Apps are also being developed for Android and iOS devices.
INDUSTRY PARTICIPATION
- Raytheon Missile Systems, Intel Corporation, NXP, Sprint, ViaSOL Energy,Aperio DSP, Poundra, PSG, Applied Core Technologies, and Interactive Flow Systems support the related graduate projects.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
* The work at Arizona State University is supported in part by the NSF DUE award 1525716 and the SenSIP Center. The work at Clarkson University is supported in part by the NSF DUE award 1525224.